The new disk defragmentations are mainly focused on the system
performance, try to minimize the number of times a disk read or write
request is issued and try to transfer data in relatively larger data
blocks. This way it improves the system performance.
So what exactly is defragmentation and how is that help the performance of my system?
During our usage of computer there will be many files come and out, hard drive is the place to shore all the files. When file A first come to the system, the operating system will try to find the largest possible continuous data blocks for the file, when it do, the file is placed on the disk. Say you need to make few changes on this file, now that the size of the file has grow larger, the problem is the extra file space are not write continuously now. Since the OS does not know how large the file will expend, hence OS will not pre-define the space file A need for size extension. The only way to store the extra information is to have it store elsewhere. This result the file fragmentation, another words the file is no longer continuous, it is broken up into parts.
The result of disk fragmentation will be the extra I/O hard drive need to perform in order to read/write the file. Moreover, this extra physical performance will reduce the speed in CPU utilization and ultimately affects your system’s performance. [Note: There are mainly two different types of fragmentation, the one we have illustrated are the External Fragmentation, to discover more click here ]
So with this said, how we do know if the file on our hard drive is broken apart or not?
To find out, we can use the build-in disk fragmentation utility.
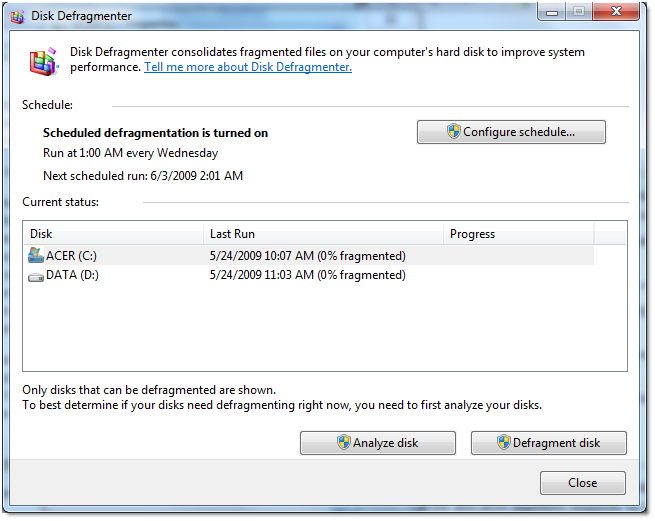
Right click the hard drive -> Properties -> Tools -> Defragmentation -> Defragment Now…
This will bring you up the UI version of defragmentation.



So what exactly is defragmentation and how is that help the performance of my system?
During our usage of computer there will be many files come and out, hard drive is the place to shore all the files. When file A first come to the system, the operating system will try to find the largest possible continuous data blocks for the file, when it do, the file is placed on the disk. Say you need to make few changes on this file, now that the size of the file has grow larger, the problem is the extra file space are not write continuously now. Since the OS does not know how large the file will expend, hence OS will not pre-define the space file A need for size extension. The only way to store the extra information is to have it store elsewhere. This result the file fragmentation, another words the file is no longer continuous, it is broken up into parts.
The result of disk fragmentation will be the extra I/O hard drive need to perform in order to read/write the file. Moreover, this extra physical performance will reduce the speed in CPU utilization and ultimately affects your system’s performance. [Note: There are mainly two different types of fragmentation, the one we have illustrated are the External Fragmentation, to discover more click here ]
So with this said, how we do know if the file on our hard drive is broken apart or not?
To find out, we can use the build-in disk fragmentation utility.
Right click the hard drive -> Properties -> Tools -> Defragmentation -> Defragment Now…
This will bring you up the UI version of defragmentation.
If you are a geek like us, you can also try to use the command line disk defragments.
To do:
- Open up the command port -> Start manual -> cmd
- Type the command “defrag”
This
will show you a list of options, for examples defrag C: /U /V this will
defrag your C drive and print out the progress and results

Just an example of my hard drive’s defragmentation

This is before,

This is after. Notice the difference in largest free space size, and average free space size? That’s a big difference.
My average free space size went from 468 KB to 19.81 MB and I’ve also extends my largest free space size.
Hopefully now your hard drive will be smooth, and increase your system performance.
Note:
there is no need to do this often; usually the process will take few
hours depending on the size of your hard drive. The larger you’re hard
drive and the more file you have on your hard drive, the longer the
process will take. If you have a SSD has your hard drive, than you might
want to consider performing less disk defragment. Since there are a
limited number of times to read and write to the SSD, disk
defragmentation will need to both read and rewrite the file, hence
result your SSD to die quicker than normal disk.
No comments:
Post a Comment